left ventricular wall thickness measurement ct|left ventricular diastolic septal thickness : Chinese To use adenosine-induced stress CT myocardial perfusion imaging (CT-MPI) to determine normal reference values for left ventricle (LV) wall thickness (WT) and motion parameters.
我们拥有数十个遍布在中国大陆所有重要港口的生产基地。. 能够提供全系列集装箱产品,并拥有完全自主知识产权的供应商。. 自1996年以来,中集的集装箱产销量一直保持世界领先地位,2007年中集成为全球集装箱行业首家年产量突破200万TEU的企业。. 未来我们 .
{plog:ftitle_list}
12 de fev. de 2024 · Join us in pioneering the future of medical coding with CAIMC ™. Embrace the AI wave and safeguard your professional journey in the ever-evolving world of healthcare. Unlock your potential with the CAIMC Course at PMBA Latest. Gain comprehensive AI Medical Coding and AI RCM Training.
Normal sex- and age-specific reference ranges for left ventricular mid-diastolic wall thickness (LV-MDWT) at prospective electrocardiographically triggered mid-diastolic CT angiography were provided, and LV-MDWT was .
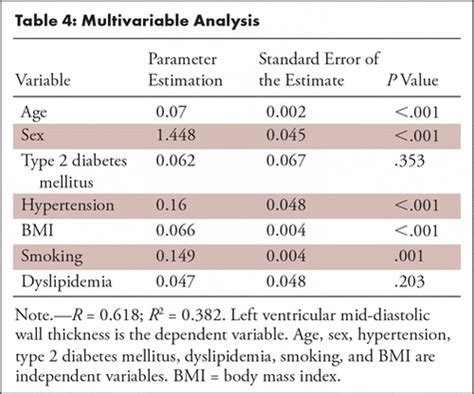
Normal sex- and age-specific reference ranges for left ventricular mid-diastolic wall thickness (LV-MDWT) at prospective electro-cardiographically triggered mid-diastolic CT angiography . After manually contouring the epicardial (green line in A–D) and endocardial (red line in A–D) border, myocardial thickness was automatically acquired in 100 measurements per left ventricular wall using the 2 . Short-axis multiplanar reformatted (MPR) images of arterial (A) and delayed-phase (B) cardiac CT show thinned myocardium with fixed subendocardial perfusion defect . LV-MDWT was measured in 2383 consecutive patients, without structural heart disease, undergoing prospective electrocardiographically (ECG) triggered mid-diastolic .
To use adenosine-induced stress CT myocardial perfusion imaging (CT-MPI) to determine normal reference values for left ventricle (LV) wall thickness (WT) and motion parameters.
To generate normal reference values for left ventricular mid-diastolic wall thickness (LV-MDWT) measured by using CT angiography. LV-MDWT was measured in 2383 consecutive patients, . CT. One publication has suggested left ventricular enlargement being able to be reliably identified on non-gated contrast-enhanced multidetector CT (with sensitivity of 78% and specificity of 100%) when the maximum .
toyota yaris 2013 side impact crash testing
normal left ventricular wall thickness
The measurement of left ventricular (LV) function is a well-established clinical parameter that has fundamental diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications. Cardiac CT angiography .The measurement of left ventricular (LV) function is a well-established clinical parameter that has fundamental diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications. Cardiac CT angiography (CCTA) and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) allow accurate LV .Left ventricular hypertrophy is a condition where the muscle wall of the heart's left pumping chamber thickens. Left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy consists in an increased LV wall thickness. . MR, mitral regurgitation; MWT, maximal wall thickness; RV, right ventricle; SAM, systolic anterior motion. . In a small case series, ECV measurements by CT and CMR were well correlated (r 2 = 0.85). ECV CT was higher in amyloidosis than aortic stenosis .
Figure 1: Images used for left ventricular (LV) mid-diastolic wall thickness and LV mass measurements. (a) Prospective electrocardiographically gated CT angiography study in mid-diastolic phase of the basal, mid, and apical (from left to right) short-axis (SAX) plane with LV wall thickness caliper measurements Left ventricular maximum wall thickness (MWT) is a key imaging biomarker in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, guiding diagnosis, risk stratification, and clinical management. 1–4 For diagnosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is clinically defined by an MWT of at least 15 mm in one or more left ventricular myocardial segments in the absence of abnormal loading .
In fact, each region of the heart has varying thickness level. For instance, Walpot, et al. [104] reported that the left ventricular of adult men and women had a mean thickness of 7.2 -8.3 mm . wall abnormalities. left ventricular aneurysm; hypertrophic cardiomyopathy / dilated cardiomyopathy; Radiographic features . left ventricular enlargement being able to be reliably identified on non-gated contrast-enhanced multidetector CT (with sensitivity of 78% and specificity of 100%) when the maximum luminal diameter of the LV is greater .
Measurement discrepancies of left ventricular mass and maximum wall thickness between modalities are clinically significant in patients with Fabry disease because use of one modality over the other could affect the diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy in 29% of patients, eligibility for disease-specific therapy in 26% of patients, and .The measurement of left ventricular (LV) function is a well-established clinical parameter that has fundamental diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications. . (EMR) data, including age, sex, and body surface area (BSA). The algorithm calculates the local values for myocardial wall thickness during end-diastole, myocardial wall .
Left ventricular mass can be further estimated based on geometric assumptions of ventricular shape using the measured wall thickness and internal diameter. [7] Average thickness of the left ventricle, . CT and MRI-based measurement can be used to measure the left ventricle in three dimensions and calculate left ventricular mass directly.Figure 1: Images used for left ventricular (LV) mid-diastolic wall thickness and LV mass measurements. (a) Prospective electrocardiographically gated CT angiography study in mid-diastolic phase of the basal, mid, and apical (from left to right) short-axis (SAX) plane with LV wall thickness caliper measurementsSince wall thickness does vary with position (the left lateral ridge being an especially thick region, whilst the posterior wall usually has a lower thickness than the anterior wall), two studies which had the same patient cohort and measuring method could have vastly differing results if different measurement regions were chosen.
Up to 30% of selected heart failure patients do not benefit clinically from cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). Left ventricular (LV) wall thickness (WT) analysed using computed tomography (CT) has rarely been evaluated in response to CRT and mitral . Purpose To generate normal reference values for left ventricular mid-diastolic wall thickness (LV-MDWT) measured by using CT angiography. Materials and Methods LV-MDWT was measured in 2383 consecutive patients, without structural heart disease, undergoing prospective electrocardiographically (ECG) triggered mid-diastolic coronary CT angiography. .i. Linear Measurements p. 2 ii. Volume Measurements p. 2 iii. LV Mass Calculations p. 3 b. Left Ventricular Function Assessment p. 4 i. Global Systolic Function Parameters p. 4 ii. Regional Function p. 5 2. Right Ventricle (RV) Size and Function p. 6 a. RV Size p. 6 Echocardiographic measurements of minor axis and wall thickness and calculations from these two measurements of left ventricular end-diastolic volume and mass were performed in 24 patients and compared with angiocardiographic measurements of the same variables in corresponding patients. The echo-measured left ventricular end-diastolic .
Methodological developments for fractal analysis of the left ventricle are ongoing . Demographic parameters. In the largest published reference cohort (n = 323) , there was no relationship between maximal non-compacted (NC)/compacted (C) wall thickness ratio and age, gender, race/ethnicity, height or weight.The gated CT scan was taken in diastole and shows the normal left ventricular dimensions which for the left ventricle wall is between .8 cms and 1.2 cms, and for the cavity is 4.5-5.5cms. the measurement should be taken at the level of the papillary muscles which is in mid ventricular cavity. code Courtesy Ashley Davidoff copyright 2018Left ventricular hypertrophy is a condition where the muscle wall of heart's left pumping chamber becomes thickened.
Schematic of left ventricular myocardial wall thickness measurement sites on vertical (A) and horizontal (B) long axis CT reconstructions. TP, thin point; AP1-4, apex measurements; A1-3, anterior wall; I1-3, inferior wall; L1-3, lateral wall Background—We sought to compare maximal left ventricular (LV) wall thickness (WT) measurements as obtained by routine clinical practice between echocardiography and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) and document causes of discrepancy. Methods and Results—One-hundred and ninety-five patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (median .IVSd, inter-ventricular septal thickness in diastole; LV, mass calculated using the linear method; LVIDd, left ventricular internal diameter in diastole; LVIDs, left ventricular internal diameter in systole; LVMi, left ventricular mass index; LVPWd, left ventricular posterior wall thickness in .
Current American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association diagnostic criteria include the identification of a hypertrophied left ventricle (LV) of wall thickness typically ≥15 mm in adults without another underlying cause. 1 Asymmetric septal hypertrophy has long been recognized as a common and distinctive feature of HCM. Purpose To generate normal reference values for left ventricular mid-diastolic wall thickness (LV-MDWT) measured by using CT angiography. Materials and Methods LV-MDWT was measured in 2383 consecutive patients, without structural heart disease, undergoing prospective electrocardiographically (ECG) triggered mid-diastolic coronary CT angiography. .The assessment of left ventricle (LV) function with cardiac CT has been validated in multiple . Reference values for quantitative left ventricular and left atrial measurements in cardiac computed tomography. Eur Radiol . Quantitative assessment of regional left ventricular wall thickness and thickening using 16 multidetector-row computed . Left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy consists in an increased LV wall thickness. . MR, mitral regurgitation; MWT, maximal wall thickness; RV, right ventricle; SAM, systolic anterior motion. . In a small case series, ECV measurements by CT and CMR were well correlated (r 2 = 0.85). ECV CT was higher in amyloidosis than aortic stenosis .
toys impact test
Let’s now review 6 pitfalls to avoid when measuring the left ventricular wall and chambers. Avoid RV Trabeculations. . Incorrect: Correct: The trabeculation was measured as part of the IVS measurement causing the thickness of the septum to be over estimated: The gains, TGCs and focus were adjusted to help clearly define the endocardial .
normal left ventricle wall thickness
tqc impact test
left ventricular wall thickness measurement
webHannahowo Photo #7001. Previous Next. Check out this sexy photo #7001 from Hannahowo.
left ventricular wall thickness measurement ct|left ventricular diastolic septal thickness